Predictive value of HBP, IL-18 combined with IL-6 for disease severity and prognosis in sepsis
-
摘要:
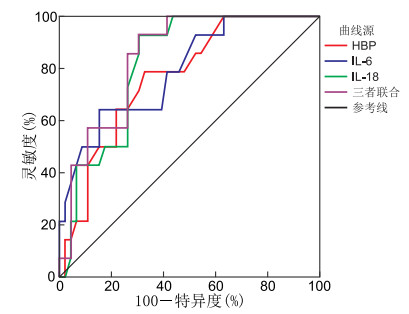
目的 脓毒症病死率高,发展迅速,为评估脓毒症患者的预后及病情分级,本研究通过分析肝素结合蛋白(HBP)、白介素-6(IL-6)及白介素-18(IL-18)的表达水平,探讨这些指标对脓毒症患者的预测价值。 方法 选取2023年1月—2024年6月蚌埠医科大学第一附属医院急诊医学科和ICU收治的80例患者。根据脓毒症诊断标准,将患者分为非脓毒症组即普通感染组20例、脓毒症组35例、脓毒症休克组25例;比较3组患者HBP、IL-18、IL-6水平;以28 d为研究终点,将脓毒症患者分为生存组和死亡组,比较2组HBP、IL-18、IL-6水平;采用Pearson分析研究HBP、IL-18、IL-6与急性生理与慢性健康状况Ⅱ评分(APACHE-Ⅱ评分)、序贯器官衰竭评分(SOFA评分)的相关性;采用ROC曲线分析HBP、IL-6、IL-18对脓毒症患者预后的评估价值。 结果 普通感染组、脓毒症组的HBP、IL-6、IL-18明显低于脓毒症休克组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001);死亡组的HBP、IL-6、IL-18明显高于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。HBP、IL-6、IL-18与SOFA评分和APACHE-Ⅱ评分呈正相关关系。HBP、IL-6、IL-18单独预测脓毒症患者预后的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.769、0.793、0.818,约登指数分别为0.460、0.491、0.553,3项指标联合预测脓毒症患者预后的ROC曲线下面积为0.842,约登指数为0.587,3项指标联合的预测价值更高。 结论 HBP、IL-6、IL-18血清水平可有效反映脓毒症患者的病情严重程度,且3种炎症因子联合检测时对脓毒症患者的预后比各指标单独检测的评估效能更高。 Abstract:Objective Sepsis is associated with high mortality and rapid progression. To evaluate the prognosis and disease severity in septic patients, this study analyzed the expression levels of heparin-binding protein (HBP), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-18 to explore their predictive value. Methods Eighty patients admitted to the Emergency Medicine Department and ICU of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University from January 2023 to June 2024 were selected. According to the diagnostic criteria of sepsis, they were divided into the non-sepsis group, namely 20 cases in the common infection group, 35 cases in the sepsis group, and 25 cases in the septic shock group. The levels of HBP, IL-18 and IL-6 in the three groups of patients were compared. Taking 28 days as the endpoint of the study, patients with sepsis were divided into the survival group and the death group, and the levels of HBP, IL-18 and IL-6 in the two groups were compared. Pearson analysis was used to compare the correlations between HBP, IL-18, IL-6 and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation-Ⅱ score (APACHE-Ⅱ) score and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score. The ROC curve was used to analyze the evaluation of the prognosis of patients with sepsis by HBP, IL-6 and IL-18. Results The HBP, IL-6 and IL-18 values of the common infection and septic group were significantly lower than the septic shock group (P < 0.001); the HBP, IL-6 and IL-18 values were significantly higher than the surviving group, respectively (P < 0.001). Moreover, HBP, IL-6 and IL-18 values showed significant positive correlation with SOFA score and APACHE-Ⅱ score. When HBP, IL-6 and IL-18 were tested separately, the area under the curve was 0.769, 0.793 and 0.818, respectively, and the Youden index was 0.460, 0.491 and 0.553, respectively. When the three indicators were tested jointly, the area under the ROC curve was 0.842 and the Youden index was 0.587, and the combined test value was higher than the single test value. Conclusion By comparing the serum levels of HBP, IL-6 and IL-18 in three groups, the severity of sepsis patients can be effectively reflected, and the combined detection of the three inflammatory factors has better evaluation efficiency than the single index alone. -
Key words:
- Heparin-binding protein /
- Interleukin-18 /
- Interleukin-6 /
- Sepsis /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 普通感染组、脓毒症组和脓毒症休克组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. General infection group, sepsis group, and septic shock group
项目 普通感染组(n=20) 脓毒症组(n=35) 脓毒症休克组(n=25) 统计量 P值 性别(男性/女性,例) 10/10 22/13 16/9 1.111a 0.292 年龄(x±s,岁) 69.60±14.75 68.68±13.65 67.76±8.27 0.120b 0.886 BMI(x±s) 24.52±2.49 23.74±2.13 23.67±2.85 0.816b 0.445 基础疾病[例(%)] 高血压 10(50.00) 13(37.14) 12(48.00) 1.122a 0.571 糖尿病 7(35.00) 10(28.57) 8(32.00) 0.254a 0.881 冠心病 5(25.00) 15(42.86) 9(36.00) 1.757a 0.415 脑梗死 6(30.00) 7(20.00) 4(16.00) 1.359a 0.507 感染部位[例(%)] 0.435a 0.427 呼吸系统 9(45.00) 20(57.14) 8(32.00) 泌尿系统 4(20.00) 5(14.29) 6(24.00) 消化系统 7(35.00) 10(28.57) 11(44.00) WBC[M(P25, P75),×109/L] 7.49(5.65, 12.57) 12.75(8.46, 15.25) 8.57(5.59, 18.37) 5.741c 0.057 CRP[M(P25, P75),mg/L] 75.42(56.85, 108.89) 117.80(65.51, 170.13) 119.32(61.25, 166.85) 4.326c 0.105 SCr(x±s,μmol/L) 101.09±25.22 94.72±17.24 103.71±19.47 0.371b 0.690 注:a为χ2值,b为F值,c为H值。 表 2 普通感染组、脓毒症组和脓毒症休克组HBP、IL-6、IL-18水平及APACHE-Ⅱ评分、SOFA评分比较(x ±s)
Table 2. HBP, IL-6, IL-18, APACHE Ⅱ score, and SOFA score in the general infection, sepsis, and septic shock group (x ±s)
组别 例数 HBP(ng/mL) IL-6(pg/mL) IL-18(pg/mL) APACHE-Ⅱ评分(分) SOFA评分(分) 普通感染组 20 37.25±1.37 44.75±2.55 87.30±5.19 脓毒症组 35 69.74±4.80a 60.25±3.95a 106.31±12.75a 15.02±2.91 7.51±1.90 脓毒症休克组 25 80.40±5.74ab 90.48±8.54ab 133.80±14.63ab 23.12±4.85 15.88±2.31 统计量 528.087c 402.232c 85.857c 8.045d 15.345d P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:与普通感染组比较,aP < 0.001;与脓毒症组比较,bP < 0.001。c为F值,d为t值。 表 3 HBP、IL-6、IL-18与APACHE-Ⅱ评分、SOFA评分的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of HBP, IL-6, and IL-18 with APACHE Ⅱ and SOFA scores
指标 APACHE Ⅱ评分 SOFA评分 r值 P值 r值 P值 IL-6 0.707 < 0.001 0.868 < 0.001 HBP 0.588 < 0.001 0.679 < 0.001 IL-18 0.735 < 0.001 0.759 < 0.001 表 4 不同预后脓毒症患者HBP、IL-6、IL-18水平和APACHE-Ⅱ评分、SOFA评分比较
Table 4. Comparison of HBP, IL-6, IL-18 levels, APACHE Ⅱ scores, and SOFA scores in sepsis patients with different prognoses
组别 例数 HBP
(x±s, pg/mL)IL-6
(x±s, pg/mL)IL-18
(x±s, pg/mL)APACHE-Ⅱ评分
(x±s, 分)SOFA评分
[M(P25, P75), 分]生存组 46 72.63±7.06 69.52±13.85 112.82±17.93 16.93±4.95 10.16(6.62,13.77) 死亡组 14 79.28±6.26 84.85±17.54 134.01±13.57 23.57±5.24 12.77(9.73, 16.95) 统计量 3.162a 3.403a 4.066a 4.339a -2.027b P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.043 注:a为t值,b为Z值。 表 5 HBP、IL-6、IL-18对脓毒症患者预后的预测效能
Table 5. Predictive efficacy of HBP, IL-6, and IL-18 for sepsis prognosis
项目 AUC 95% CI P值 截断值 约登
指数灵敏度
(%)特异度
(%)HBP 0.769 0.640~0.898 < 0.001 74.5 0.460 78.6 67.4 IL-6 0.793 0.661~0.924 < 0.001 87.0 0.491 85.7 69.6 IL-18 0.818 0.711~0.920 < 0.001 121.5 0.553 64.3 84.8 三者联合 0.842 0.741~0.942 < 0.001 0.587 92.9 65.2 -
[1] ZHANG Y Y, NING B T. Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 407. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00816-9. [2] SUN B S, LEI M X, ZHANG J Q, et al. Acute lung injury caused by sepsis: how does it happen?[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2023, 10: 1289194. DOI10.3389/fmed. 2023.1289194. [3] BARICHELLO T, GENEROSO J S, SINGER M, et al. Biomarkers for sepsis: more than just fever and leukocytosis: a narrative review[J]. Crit Care, 2022, 26(1): 14. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03862-5. [4] CONG S, MA T G, DI X, et al. Diagnostic value of neutrophil CD64, procalcitonin, and interleukin-6 in sepsis: a meta-analysis[J]. BMC Infect, 2021, 21(1): 384. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06064-0. [5] OTHMAN A, SEKHERI M, FILEP J G. Roles of neutrophil granule proteins in orchestrating inflammation and immunity[J]. FEBS J, 2022, 289(14): 3932-3953. doi: 10.1111/febs.15803 [6] 冯立伟, 王婕莹, 王洪亮, 等. 肝素结合蛋白在重症患者中的临床应用[J]. 中国急救医学, 2023, 43(7): 579-584.FENG L W, WANG J Y, WANG H L, et al. Clinical application of heparin-binding protein in severe patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine, 2023, 43(7): 579-584. [7] 李璐, 李文强, 胡念丹, 等. 血清IL-18水平评估脓毒症患者病情严重程度的价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2022, 17(2): 221-224, 229.LI L, LI W Q, HU N D, et al. The value of serum IL-18 level in evaluating the severity of sepsis[J]. China Journal of Emergency Resuscitation and Disaster Medicine, 2022, 17(2): 221-224, 229. [8] EVANS L, RHODES A, ALHAZZANI W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 49(11): 1181-1247. [9] PIERRAKOS C, VELISSARIS D, BISDORFF M, et al. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 287. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-02993-5. [10] IHIM S A, ABUBAKAR S D, ZIAN Z, et al. Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 919973. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.919973. [11] 曹轮飞, 程亚辉, 赵振东. 脓毒症患者血清PCT和IL-10及IL-18水平及其预后价值分析[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2023, 44(16): 35-39.CAO L F, CHENG Y H, ZHAO Z D, et al. Analysis of serum levels of PCT, IL-10, and IL-18 and their prognostic values in patients with sepsis[J]. Journal of Medical Forum, 2023, 44(16): 35-39. [12] WU Y L, YO C H, HSU W T, et al. Accuracy of heparin-binding protein in diagnosing sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Crit Care Med, 2021, 49(1): e80-e90. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004738 [13] 景丽丽, 张玉伟, 刘彬, 等. 血清HMGB1、HBP、IL-10水平预测脓毒症预后的临床价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2023, 33(1): 31-34.JING L L, ZHANG Y W, LIU B, et al. Clinical value of serum HMGB1, HBP and IL-10 in prediction of prognosis of patients with sepsis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2023, 33(1): 31-34. [14] FISHER J, KAHN F, WIEBE E, et al. The dynamics of circulating heparin-binding protein: implications for its use as a biomarker[J]. J Innate Immun, 2022, 14(5): 447-460. doi: 10.1159/000521064 [15] 李璐, 吴优, 史娟娟. 血清PTX3、HBP、PGRN水平与产褥期细菌感染所致脓毒症的关联性分析[J]. 淮海医药, 2023, 41(4): 352-355.LI L, WU Y, SHI J J, et al. Expression of PTX 3, HBP and PGRN in patients with sepsis induced by puerperal bacterial infection and its clinical significance[J]. Journal of Huaihai Medicine, 2023, 41(4): 352-355. [16] KATSAROS K, RENIERIS G, SAFARIKA A, et al. Heparin binding protein for the early diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis in the emergency department: the prompt multicenter study[J]. Shock, 2022, 57(4): 518-525. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001900 [17] 高怡宁, 李明晖. 血清标志物在细菌及病毒性脓毒症鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. 浙江医学, 2022, 44(1): 21-24.GAO Y N, LI M H. Value of serum markers in differential diagnosis of bacterial and viral sepsis[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal, 2022, 44(1): 21-24. [18] SCHMIDT-ARRAS D, ROSE-JOHN S. Endosomes as signaling platforms for IL-6 family cytokine receptors[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 688314. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.688314. [19] 牛凯旋, 吴淑璐, 刘成, 等. 血清淀粉样蛋白A和白细胞介素-6对脓毒症诊断及病情严重程度评估的临床价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(9): 1484-1487. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002629NIU K X, WU S L, LIU C, et al. Clinical value of serum amyloid A and interleukin-6 in the diagnosis and severity evaluation of sepsis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2022, 20(9): 1484-1487. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002629 [20] HIRANO T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer[J]. Int Immunol, 2021, 33(3): 127-148. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxaa078 [21] 段莉莉, 段榆琳, 刘艳. 脓毒症患者白细胞计数、血清C反应蛋白、肝素结合蛋白、降钙素原表达及与病情进展及预后关系[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2024, 23(6): 589-592.DUAN L L, DUAN Y L, LIU Y, et al. Expression of white blood cell count, serum C-reactive protein, heparin binding protein, and procalcitonin in sepsis patients and their relationship with disease progression and prognosis[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 2024, 23(6): 589-592. -





 下载:
下载: