Construction and verification of prediction model and treatment strategy for shunt loss after portal hypertension TIPS
-
摘要:
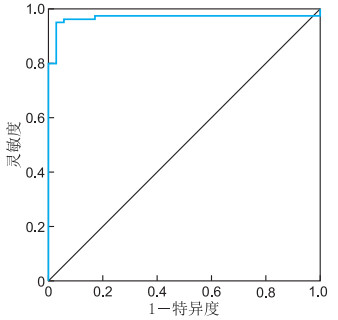
目的 明确门静脉高压患者行经颈静脉门体分流术(TIPS)术后分流道失功的影响因素,构建并验证临床预测模型,并针对不同类型的分流道失功制定相应的处理对策,为患者提供合理的治疗方案。 方法 回顾性分析2020年1月—2024年12月在蚌埠医科大学第一附属医院介入科接受TIPS治疗的120例门静脉高压患者的临床资料。根据术后随访结果分为分流道失功组(35例)和未失功组(85例)。将差异有统计学意义的变量纳入多因素logistic回归分析,分析影响分流道失功的独立危险因素,并基于此构建预测模型。通过ROC曲线评估模型区分度;针对不同类型的分流道失功提出相应处理对策。 结果 多因素logistic回归分析表明,抗凝治疗(OR=15.754, P=0.030)、门静脉血栓(OR=0.052, P=0.008)及门静脉穿刺部位(OR=0.064, P=0.007)为TIPS术后分流道失功的独立影响因素。构建模型的ROC曲线下面积(95% CI)为0.933(0.882~0.983),最佳界值为0.866,此时灵敏度为0.894, 特异度为0.971。 结论 抗凝治疗、门静脉血栓及门静脉穿刺部位是TIPS术后分流道失功的独立影响因素,据此构建的预测模型可帮助临床医生早期进行风险分层并采取干预措施。 Abstract:Objective To identify the risk factors of shunt dysfunction after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in patients with portal hypertension, to construct and verify the clinical prediction model, and to formulate corresponding countermeasures for different types of shunt dysfunction, so as to provide reasonable treatment for patients. Methods The clinical data of 120 patients who underwent TIPS in the interventional department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University from January 2020 to December 2024 were retrospectively analyzed. Subsequent to the surgical procedure, the subjects were categorized into two distinct groups, namely the shunt dysfunction group and the non-dysfunction group, with the respective numbers amounting to 35 and 85 cases. Variables with significant differences were included in multivariate logistic regression analysis to determine the independent risk factors, and a prediction model was constructed based on this. The discrimination capacity of the model was evaluated by means of the ROC curve. Finally, the corresponding countermeasures are proposed for the various types of shunt failure. Results Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that anticoagulation therapy (OR=15.754, P=0.030), portal vein thrombosis (OR=0.052, P=0.008) and portal vein puncture site (OR=0.064, P=0.007) were independent influencing factors for shunt dysfunction after TIPS. The area under the ROC curve (95% CI) of the constructed model was 0.933 (0.882-0.983), and the corresponding optimal cut-off value was 0.866. The sensitivity was 0.894, and the specificity was 0.971. Conclusion Therapy, portal vein thrombosis and portal vein puncture site are independent influencing factors of shunt dysfunction after TIPS. The prediction model constructed accordingly has the potential to assist clinicians in the early identification of risks and the implementation of intervention measures. -
表 1 分流道失功组与未失功组门静脉高压患者各项目比较
Table 1. Comparison of parameters between shunt dysfunction and non-dysfunction groups in portal hypertension patients
项目 分流道失功组(n=35) 未失功组(n=85) 统计量 P值 年龄(x±s,岁) 55.26±11.29 56.58±11.00 0.593a 0.555 性别[例(%)] 0.048b 0.827 男性 24(68.57) 60(70.59) 女性 11(31.43) 25(29.41) 白蛋白(x±s,g/dL) 30.95±6.35 31.85±6.50 0.696a 0.488 总胆红素[M(P25, P75), mg/dL] 19.30(14.50, 24.10) 21.50(14.60, 30.50) -0.546c 0.585 肌酐[M(P25, P75), mmol/L] 61.00(55.30, 72.60) 62.30(51.95, 74.70) -0.387c 0.699 PT[M(P25, P75), s] 15.30(14.60, 17.00) 15.80(14.30, 17.50) -0.332c 0.740 AST[M(P25, P75), U/L] 35.80(25.00, 53.00) 33.00(22.00, 42.95) -1.588c 0.112 ALT[M(P25, P75), U/L] 28.10(19.00, 47.00) 29.30(19.00, 43.50) -0.447c 0.655 PLT[M(P25, P75), ×109/L] 92.00(60.00, 146.00) 76.00(48.50, 107.50) -1.432c 0.152 WBC[M(P25, P75), ×109/L] 5.77(3.63, 9.67) 4.90(2.95, 8.41) -1.365c 0.172 INR[M(P25, P75)] 1.29(1.19, 1.46) 1.33(1.22, 1.49) -0.921c 0.357 糖尿病[例(%)] 97.895b < 0.001 否 1(2.86) 81(95.29) 是 34(97.14) 4(4.71) 腹水[例(%)] 1.522b 0.217 否 13(37.14) 22(25.88) 是 22(62.86) 63(74.12) 门静脉血栓[例(%)] 89.538b < 0.001 否 2(5.71) 80(94.12) 是 33(94.29) 5(5.88) 抗凝治疗[例(%)] 97.895b < 0.001 否 34(97.14) 4(4.71) 是 1(2.86) 81(95.29) 脾切除(栓塞)史[例(%)] 85.984b < 0.001 否 2(5.71) 79(92.94) 是 33(94.29) 6(7.06) 门静脉穿刺部位[例(%)] 85.984b < 0.001 非右支 2(5.71) 79(92.94) 右支 33(94.29) 6(7.06) CT静脉曲张kim分级[M(P25, P75),级] 3.00(3.00, 3.00) 3.00(3.00, 3.00) -0.216c 0.829 Child分级[M(P25, P75),级] 2.00(2.00, 2.00) 2.00(2.00, 2.00) -0.422c 0.673 注:a为t值,b为χ2值,c为Z值。 表 2 门静脉高压患者TIPS术后分流道失功影响因素的logistic回归分析
Table 2. Logistic regression analysis of factors influencing shunt dysfunction after TIPS in patients with portal hypertension
变量 B SE Waldχ2 P值 OR值 95% CI 抗凝治疗 2.757 1.274 4.683 0.030 15.754 1.297~191.387 门静脉血栓 -2.957 1.106 7.143 0.008 0.052 0.006~0.455 门静脉穿刺部位 -2.749 1.011 7.397 0.007 0.064 0.009~0.464 截距 2.610 1.204 4.700 0.030 13.597 1.285~143.904 -
[1] 陈松, 史键山. 急诊介入栓塞治疗对急性重度静脉曲张上消化道出血的临床价值研究[J]. 新医学, 2022, 53(9): 643-648.CHEN S, SHI J S. Clinical value of emergency interventional therapy for acute severe variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Journal of New Medicine, 2022, 53(9): 643-648. [2] 陈金强, 李春达, 李富强, 等. 肝硬化失代偿期患者并发自发性腹膜炎的危险因素分析及治疗[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(7): 1131-1134. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002003CHEN J Q, LI C D, LI F Q, et al. Analysis and treatment of the risk factors for spontaneous peritonitis in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2021, 19(7): 1131-1134. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002003 [3] KARAGIANNAKIS D S. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for recompensating decompensated cirrhosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30(20): 2621-2623. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2621 [4] 朱军源, 夏翊夫, 杜艳梅, 等. 经皮经肝胃冠状静脉栓塞术单独或联合部分脾动脉栓塞术治疗肝硬化门静脉高压出血效果比较的Meta分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(1): 89-95.ZHU J Y, XIA Y F, DU Y M, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous transhepatic variceal embolization alone or in combination with partial splenic embolization in treatment of portal hypertensive hemorrhage in liver cirrhosis: a meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2024, 40(1): 89-95. [5] 陈沅然, 黎铭恩, 刘序友, 等. 血氨对肝硬化食管静脉曲张的诊断价值[J]. 新医学, 2022, 53(4): 283-286.CHEN Y R, LI M E, LIU X Y, et al. Diagnostic value of serum ammonia for esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients[J]. Journal of New Medicine, 2022, 53(4): 283-286. [6] 张雨婷, 沈炜, 顾佳萍. IL-33、TIMP-1、MMP-2与慢性乙型肝炎肝硬化预后的相关性分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2025, 23(2): 231-234. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003874ZHANG Y T, SHEN W, GU J P, et al. The correlation between IL-33, TIMP-1, MMP-2 and prognosis of chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2025, 23(2): 231-234. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003874 [7] 孙清, 刘芳, 刘德嘉, 等. 肝硬化门静脉高压患者TIPS术后门静脉分支远端血栓形成相关因素及其对预后的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2024, 24(11): 2125-2129.SUN Q, LIU F, LIU D J, et al, Related factors of distal portal vein thrombosis and its effect on prognosis in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension after TIPS[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2024, 24(11): 2125-2129. [8] ZHU P, DONG S T, SUN P, et al. Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE)-covered stents versus bare stents for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in people with liver cirrhosis[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2023, 8(8): 1465-1858. [9] 赖瑞敏, 朱月永. 门静脉高压症: 经颈静脉肝内门体分流术的合理应用及其相关并发症的预防和处理[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26(1): 4-7.LAI R M, ZHU Y Y. Portal hypertension: indication of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and the prevention of related complications[J]. Journal of Practical Hepatology, 2023, 26(1): 4-7. [10] WAIDYARATNE G, JALIL S, LIU A, et al. Utility of advanced age as a predictor of outcomes in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2025. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-025-08940-0. [11] ZHOU G P, JIANG Y Z, SUN L Y, et al. Early transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for acute variceal bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(7): 5390-5399. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07525-x [12] WEERATUNGA S, NAMBIAR M, HANDLEY C, et al. Refractory portal hypertension complications successfully managed by parallel transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): a case report[J]. CVIR Endovasc, 2022, 5(1): 20. DOI: 10.1186/s42155-022-00297-z. [13] 孔德元, 更藏尖措, 颜小明, 等. 利伐沙班预防TIPS术后血栓的安全性和有效性[J]. 肝胆胰外科杂志, 2023, 35(8): 464-468.KONG D Y, GENG Z J C, YAN X M, et al. Safety and efficiency of rivaroxaban in prevention of thrombosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for cirrhotic gastric varices bleeding[J]. Journal of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, 2023, 35(8): 464-468. [14] 王乐, 郭晓钟, 祁兴顺. 肝硬化门静脉血栓的临床评估与治疗: 当前观点[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023, 48(1): 18-26.WANG L, GUO X Z, QI X S. Clinical assessment and treatment of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: current perspectives[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People' s Liberation Army, 2023, 48(1): 18-26. [15] 王慧群, 叶超, 许朝, 等. 肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血内镜治疗后再出血的5年随访研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(22): 3155-3159.WANG H Q, YE C, XU C, et al. A 5-year follow-up study of rebleeding after endoscopic treatment of esophageal gastric varices rebleeding associated with liver cirrhosis[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine, 2024, 40(22): 3155-3159. [16] 李如春, 胡继红, 潘文秋, 等. TIPS治疗肝硬化伴或不伴门静脉血栓临床对比研究[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2024, 33(10): 1101-1106.LI R C, HU J H, PAN W Q, et al. TIPS for the treatment of cirrhosis with or without portal vein thrombosis: a comparative study[J]. Journal of Interventional Radiology, 2024, 33(10): 1101-1106. [17] CUSUMANO C, GUSSAGO S, GUERRA M, et al. Management of spontaneous portosystemic shunts at the time of liver transplantation: treatment or observation? Results of a systematic review[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16(5): 983-992. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10377-w [18] SENZOLO M, GARCIA-TSAO G, GARCÍA-PAGÁN J C. Current knowledge and management of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(2): 442-453. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.029 [19] MA J Q, LUO J J, ZHANG W, et al. The influence of shunting left/right portal vein branch on post-TIPS hepatic encephalopathy: a study protocol for multicenter randomized blinded controlled trial[J]. Trials, 2023, 24(1): 312. DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07326-9. [20] LUO S H, ZHOU M M, CAI M J, et al. Reduction of portosystemic gradient during transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt achieves good outcome and reduces complications[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(15): 2336-2348. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2336 [21] 李芳, 谭岁赛, 夏华, 等. 经颈静脉肝内门体分流联合胃冠状静脉栓塞术的应用进展[J]. 中国血管外科杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(4): 377-380.LI F, TAN S S, XIA H, et al. Application progress of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt combined with gastric coronary vein embolization[J]. Chinese Journal of Vascular Surgery (Electronic Version), 2021, 13(4): 377-380. -





 下载:
下载: