Mechanism of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in the early stage severe acute pancreatitis rats
-
摘要:
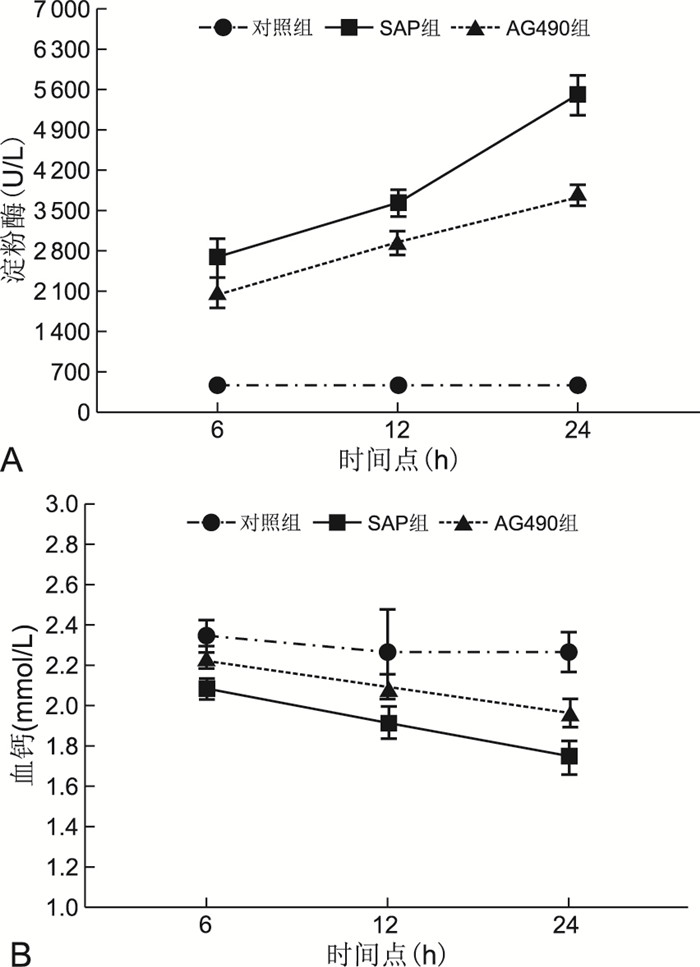
目的 探讨抑制JAK/STAT信号通路对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎(SAP)早期相关疾病指标的影响,从而推测该信号通路在SAP大鼠中可能的作用机制。 方法 将54只成年SD大鼠按随机数字表分成对照组、SAP组、AG490组,每组18只,AG490组造模前给予AG490,其他组给予等量生理盐水,以5%牛磺胆酸钠逆行胆胰管内注射法制作SAP模型,造模后6、12、24 h每组分别处死6只大鼠,取心房血测血淀粉酶、血钙、TNF-α、IL-1、IL-6,留取胰腺组织行HE染色病理检查及Western blotting法检测胰腺组织中STAT3蛋白表达水平。 结果 AG490组在6、12、24 h淀粉酶值分别为(2 049.17±257.00)U/L、(2 915.00±188.42)U/L、(3 746.50±181.05)U/L,高于对照组、低于SAP组,SAP组高于对照组(均P<0.05);AG490组6、12、24 h血钙浓度高于SAP组, 2组均低于对照组(均P<0.05);AG490组6、12、24 h TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1均低于SAP组,2组均高于对照组;SAP组胰腺组织STAT3表达量随时间增加,24 h明显高于AG490组,其他时间点差异不明显。SAP组、AG490组胰腺病理切片可见胰腺细胞水肿、炎性细胞浸润,差异不明显。 结论 SAP早期阶段可能是通过JAK/STAT信号通路诱导多种炎性因子分泌,促进胰腺炎的进展。 -
关键词:
- 重症急性胰腺炎 /
- 酪氨酸蛋白激酶 /
- 信号转导及转录激活因子 /
- 信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of inhibiting JAK/STAT signaling pathway on relevant disease indicators in rats with early stage severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), so as to speculate the possible mechanism of this signaling pathway in SAP rats. Methods Fifty-four adult SD rats were divided into control group, SAP group and AG490 group according to random number table, 18 rats in each group. AG490 group was given AG490 application before modeling, other groups were given equal amount of saline. SAP model was made by retrograde intra-biliary pancreatic duct injection with 5% sodium taurocholate, and the rats were executed at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h after modeling, and atrial blood was taken to measure serum amylase, calcium, TNF-α and calcium. The pancreatic tissues were examined by HE staining. Western blotting was used to detect the expression level of STAT3 protein in pancreatic tissues. Results The amylase values in the AG490 group at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h were (2 049.17±257.00) U/L, (2 915.00±188.42) U/L and (3 746.50±181.05) U/L, respectively, which were higher than those in the control group and lower than those in the SAP group, and SAP group was higher than the control group (all P < 0.05). The blood calcium concentrations at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h in the AG490 group were higher than those in the SAP group, both groups were lower than the control group (all P < 0.05). The TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1 at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h in the AG490 group were lower than those in the SAP group, and both groups were higher than the control group. STAT3 expression in SAPgrouppancreatic tissue increased with time between groups, and the 24 h point was significantly higher than the AG490 group, with insignificant differences at other points. AG490 group, pancreatic cell edema and inflammatory cell infiltration were seen in pathological sections, no significant difference. Conclusion The early stage of severe acute pancreatitis may induce multiple inflammatory factors through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and promote the progression of pancreatitis. -
表 1 各组大鼠血清淀粉酶、血钙水平比较(x ±s)
Table 1. Comparison of serum amylase and blood calcium in each group(x ±s)
组别 只数 淀粉酶(U/L) 血钙(mmol/L) 6 h 12 h 24 h F值 P值 6 h 12 h 24 h F值 P值 对照组 18 448.00±95.12 445.17±67.74 412.17±84.31 1.327 0.308 2.35±0.08 2.27±0.21 2.27±0.10 0.669 0.518 SAP组 18 2 666.83±328.01a 3 627.67±229.53ac 5 517.33±337.93acd 114.500 <0.001 2.09±0.05a 1.92±0.08ac 1.75±0.08acd 28.067 <0.001 AG490组 18 2 049.17±257.00ab 2 915.00±188.42abc 3 746.50±181.05abcd 147.130 <0.001 2.22±0.08ab 2.10±0.06abc 1.97±0.07abcd 15.767 <0.001 F值 129.213 541.207 784.972 18.787 10.742 61.517 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:淀粉酶,F时点=218.636,F组间=1 191.202,F交互=70.450,均P<0.05;血钙,F时点=21.143,F组间=69.163,均P<0.05,F交互=2.466, P=0.076。与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与SAP组比较,bP<0.05;与同组6 h比较,cP<0.05;与同组12 h比较, dP<0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠血清TNF-α、IL-1、IL-6水平比较(x ±s, ng/L)
Table 2. Comparison of serum TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 levels in rats of each group(x ±s, ng/L)
组别 只数 TNF-α 6 h 12 h 24 h F值 P值 对照组 18 89.33±5.39 86.67±8.29 85.00±4.05 0.601 0.567 SAP组 18 286.50±12.06a 333.33±10.69ac 445.67±35.68acd 105.600 <0.001 AG490组 18 145.17±9.60ab 276.67±14.68abc 406.33±18.40abcd 406.350 <0.001 F值 696.956 754.183 432.795 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 组别 只数 IL-6 6 h 12 h 24 h F值 P值 对照组 18 52.83±10.30 56.83±8.93 59.17±5.95 0.811 0.472 SAP组 18 321.17±6.62a 371.50±22.90ac 463.33±22.91acd 76.511 <0.001 AG490组 18 142.17±10.61ab 251.33±15.53abc 370.83±22.76abcd 283.082 <0.001 F值 1280.277 537.023 748.312 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 组别 只数 IL-1 6 h 12 h 24 h F值 P值 对照组 18 10.67±1.69 11.49±1.34 11.87±2.13 1.130 0.361 SAP组 18 87.00±10.41a 126.47±8.15ac 108.72±15.63acd 16.427 <0.001 AG490组 18 31.53±3.65ab 73.17±11.42abc 39.02±6.39abcd 44.406 <0.001 F值 224.934 299.837 155.154 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:TNF-α,F时点=384.992,F组间=1 097.802,F交互=121.961;IL-6,F时点=282.182,F组间=2 229.541,F交互=75.289;IL-1,F时点=48.709,F组间=666.874,F交互=13.290,均P<0.05。与对照组比较,aP<0.05;与SAP组比较,bP<0.05;与同组6 h比较,cP<0.05;与同组12 h比较, dP<0.05。 -
[1] FEI S K, LI W, XIANG L, XIE X W, et al. Protective effect of alprostadil on acute pancreatitis in rats via inhibiting Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/STAT3 signal transduction pathway[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 7694-7701. DOI: 10.12659/MSM.919148. [2] 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2021)[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2021, 59(7): 578-587. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20210416-00172Pancreatic Surgery Group, Surgery Society of Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis (2021)[J]. Chinese Journal of Surgery, 2021, 59(7): 578-587. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20210416-00172 [3] MONTERO P, MILARA J, ROGER I, et al. Role of JAK/STAT in interstitial lung diseases; molecular and cellular mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22: 6211. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126211. [4] CAO W Y, YANG D L, HOU S L. PCT、IL-6、hs-CRP对急性胰腺炎的诊断价值[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2019, 16(23): 3441-3443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2019.23.014 [5] QIN L Y, WANG G X. 乌司他丁联合生长抑素对重症急性胰腺炎大鼠血清炎性细胞因子的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2015, 14(15): 1225-1228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2015.015.001 [6] SU Z H, ZHENG L F, YANG H C. 早期血液滤过治疗急性重症胰腺炎合并间隔室综合征的疗效及对其血清IL-6、IL-8水平变化的影响[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2017, 11(20): 21-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYY201720009.htm [7] WANG J F, LI N, LUO Q. 腹腔镜手术治疗重症急性胰腺炎及对TNF-α、IL-6和sIL-2R水平的影响[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2017, 23(11): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1989.2017.11.015 [8] 齐宏, 陈广, 王渊文, 等. 异甘草酸镁联合奥曲肽治疗急性胰腺炎的临床疗效及对hs-CRP、IL-1β、IL-6水平的影响[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2020, 36(3): 520-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZXX202003033.htmQI H, CHEN G, WANG Y W, et al. Effects of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate combined with octreotide on acute pancreatitis and its effect on hs-CRP、IL-1β、IL-6 levels[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2020, 36(3): 520-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZXX202003033.htm [9] 刘胜新, 徐军辉, 蔡涛, 等. IL-1β在急性胰腺炎时肝损伤中的作用[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2019, 27(9): 777-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2019.09.017LIU S X, XU J H, CAI T, et al. The role of IL-1β in the acute pancreatitis with hepatic function damage[J]. Journal of Clinical Surgery, 2019, 27(9): 777-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2019.09.017 [10] 沈银峰, 巴元明, 金文银, 等. JAK2-STAT3信号通路在急性坏死性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺损伤与全身炎症反应中的作用[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2019, 19(3): 185-189. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.03.007SHEN Y F, BA Y M, JIN W Y, et al. Role of JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway in pancreatic injury and systematic inflammatory response in rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Pancreatology, 2019, 19(3): 185-189. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.03.007 [11] 陈平, 姚玮艳, 章永平, 等. 雨蛙素诱导的急性胰腺炎体外细胞模型的信号转导通路研究[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2018, 10(4): 272-275.CHEN P, YAO W Y, ZANG Y P, et al. Expression of janus kinase 1/signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 signaling pathway in cerulean stimulated pancreatic acinar cells[J]. Chinese J Ournal of Pancreatology, 2018, 10(4): 272-275. [12] WANG G L, ZHANG J C, DUI D H, et al. High mobility group box 1 induces the activation of the Janus kinase 2 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) signaling pathway in pancreatic acinar cells in rats, while AG490 and rapamycin inhibit their activation[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2016, 16(4): 307-312. [13] QIN M Z, QIN M B, LIANG Z H, et al. Effect of SOCS3 on lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis through regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(22): 10123-10131. [14] YANG X, GENG H, YOU L, et al. Rhein protects against severe acute pancreatitis in vitro and in vivo by regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 778221. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.778221. [15] ZHU S J, ZHANG C, WENG Q, et al. Curcumin protects against acute renal by suppressing JAK2/STAT3 pathway in severe acute pancreatitis in rats[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(2): 1669-1674. [16] LI M L, ZHANG X H, WANG B, et al. Effect of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway on liver injury associated with severe acute pancreatitis in rats[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(3): 2013-2021. [17] 张剑, 魏殿军. 血淀粉酶、胰脂肪酶、PCT、CRP联合检测在急性胰腺炎中的诊断价值[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2017, 21(5): 778-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD201705005.htmZHANG J, WEI D J. Clinical significance of the combined detection of AMY, LPS, PCT and CRP in prognosis of acute pancreatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis, 2017, 21(5): 778-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD201705005.htm -





 下载:
下载: